The long hunted sterile neutrino cannot be traced
Some of the most abundant particles in the universe are the so-called ghost particles, neutrinos, which travel through virtually anything on their journey through the universe. Researchers have identified three types of neutrinos, but they have been searching for one more type, an even more ghostlike sterile neutrino, which would explain mysterious phenomena like dark matter. After analysing thousands of neutrinos in the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole, researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute can now confirm that there is no evidence for the existence of sterile neutrinos. The results are published in the scientific journal, Physical Review Letters.

Morten Medici, Ph.D.-student at the Niels Bohr Institute seen in front of the IceCube Lab at the South Pole, where the temperature can reach minus 70 degree Celcius, and some of the harshest winds blows. The IceCube Neutrino Observatory consists of 5160 light sensors, frozen in the dark clear ice two kilometers beneath the surface. Here they detect the faint light from the ghost-like neutrinos. The signals from all the sensors are collected in the IceCube Lab, where the data is processed and transmitted via satellite to researches all over the world. (Credit: Morten Medici)
Neutrinos are a type of particles called ‘ghost particles’, because they hardly ever interact with matter, passing undisturbed through everything in their path through the universe. Neutrinos are very light particles and for many years it was believed that they were completely massless, but we now believe that they each have a specific mass, though it is extremely small – less than one millionth of the mass of an electron.
Changeable neutrinos
When particles (protons) with high energy – from violent events in the cosmos, for example supernovae, which are exploding stars and quasars, which are active black holes – hit the Earth’s atmosphere, a shower of particles is created, including neutrinos. The particles interact with matter and are stopped by the Earth, while the neutrinos do not interact and therefore pass straight through the Earth.
The neutrinos that are created when high-energy particles hit the Earth’s atmosphere consist of two types: muon and electron neutrinos. But neutrinos are constantly changing from one type to another. When they travel the 13,000 km through the Earth, they undergo quantum fluctuations and change into three types along the way: muon, electron and tau neutrinos.
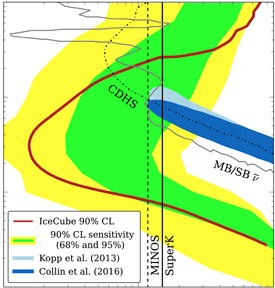
The IceCube result excludes a sterile neutrino with a mass difference (Δm^2) and oscillation with the conventional neutrinos (θ_{24}) values to the right of the red line. The IceCube exclusion rules outs the allowed region from other experiments which have ‘hints’ of a sterile neutrino; shown as the blue regions. (Credit: IceCube Collaboration)
But researchers are looking for a fourth type of neutrino, a sterile neutrino. In experiments around the world, there have been indications of such a fourth type of neutrino. A sterile neutrino may have different properties, including only interacting by means of gravity.
“One or more types of sterile neutrinos could help solve a number of mysteries, such as why there is more matter than antimatter in the universe. A sterile neutrino could provide an explanation for this imbalance, which currently cannot be explained by the three known neutrinos. A sterile neutrino with gravity could also shed light on the mysterious dark matter,” explains Jason Koskinen, assistant professor at the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen.
Detecting neutrinos
The neutrinos that are formed over the North Pole travel straight through the Earth and a minute proportion of them hit the ice at the South Pole, where the collisions are recorded in the IceCube detector, which consists of 5,160 light sensors that are frozen deep in Antarctica’s extremely clear ice.
“We have analysed hundreds of thousands of neutrinos, which after having passed through the Earth from the Northern Hemisphere have hit the ice on the South Pole, where the collisions have been recorded in the IceCube detector. We know of three neutrino types and our international team of researchers has been looking for signals from a fourth neutrino type, the so-called sterile neutrinos. For years, there has been a global mystery about the existence of a sterile neutrino with a mass of about 1 eV. If it existed, it would produce a clear signal at a certain energy interval, but we have not seen a single signal that could come from such a sterile neutrino,” explains Jason Koskinen, assistant professor and group leader in the IceCube research group at the Niels Bohr Institute and team chairman of the IceCube international research team on neutrino oscillations.

A photo of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory at the South Pole, overlaid by a plot of the neutrino transformations where the red region in the left hand side shows the signal of the proposed fourth neutrino. However, this signal did not show up in the analysis by IceCube, and hence the existence of this type of sterile neutrino can be excluded. (Credit: IceCube Collaboration)
The theory has been that this particular sterile neutrino with a mass of about 1 eV could also be formed during the quantum fluctuations that constantly cause the neutrinos to change between being myon, electron and tau neutrinos. If there was such a fourth option for conversion, it should be detectable in the IceCube detector – even if they could not be directly detected.
Jason Koskinen explains that when they cannot demonstrate the possibility of the sterile neutrinos it is done by a method of elimination. They know how many neutrinos are formed in the atmosphere from measurements in the Northern Hemisphere. In the Southern Hemisphere, the IceCube detector can detect the neutrinos when they have passed through the Earth.
“We can detect the quantity of muon, electron and tau neutrinos and is simply nothing ‘missing’ in the equation, so the conclusion is that the IceCube results weaken the possibility that this particular fourth neutrino exists. However, IceCube does not exclude the hypothetical possibility of other types of sterile neutrinos in the universe,” says Jason Koskinen.

Jason Koskinen, Assistant Professor in the IceCube research group at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, +45 2128-9061, koskinen@nbi.ku.dk
Morten Medici, PhD student in the IceCube research group at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, +45 3532-5454, mobile: +45 6151-6454, mmedici@nbi.ku.dk

