News on Astronomy in 2014
Green light for construction of the E-ELT
4 December 2014
 The ESO Council has now decided to start building the new large European telescope E-ELT (European Extremely Large Telescope) on 1 January 2015. This begins the first phase of construction of the world’s largest telescope – with Danish
The ESO Council has now decided to start building the new large European telescope E-ELT (European Extremely Large Telescope) on 1 January 2015. This begins the first phase of construction of the world’s largest telescope – with Danish
Using supermassive black holes to measure cosmic distances
26 November 2014
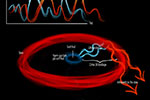 One of the major problems in astronomy is measuring very large distances in the universe. The current most common methods measure relative distances, but now research from the Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates that precise distances
One of the major problems in astronomy is measuring very large distances in the universe. The current most common methods measure relative distances, but now research from the Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates that precise distances
Mystery of dwarf galaxy could be ejected black hole
19 November 2014
 Astronomers have observed a mysterious phenomenon, which could be a massive black hole that has been ejected into space in connection with two galaxies colliding. This may be due to gravitational waves from the collision.
Astronomers have observed a mysterious phenomenon, which could be a massive black hole that has been ejected into space in connection with two galaxies colliding. This may be due to gravitational waves from the collision.
New Danish telescope for researching stars and Earth-like exoplanets
21 October 2014
 The first telescope in the Danish led telescope network will be officially opened on 25 October, 2014 on Tenerife. This will launch a worldwide stellar research project that will bring us even closer to the stars and closer to finding earth-like
The first telescope in the Danish led telescope network will be officially opened on 25 October, 2014 on Tenerife. This will launch a worldwide stellar research project that will bring us even closer to the stars and closer to finding earth-like
Comet headed for Mars
17 October 2014
 On Sunday evening, 19 October 2014 at 20:30, a comet will come closer to colliding with Mars than we have ever seen. When the comet, Siding Spring, was discovered in January 2013 it initially appeared that it might be on a direct collision
On Sunday evening, 19 October 2014 at 20:30, a comet will come closer to colliding with Mars than we have ever seen. When the comet, Siding Spring, was discovered in January 2013 it initially appeared that it might be on a direct collision
NBI researchers part of new NASA Mars mission
8 August 2014
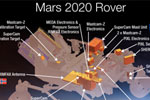 Has there been life on Mars? – and when a manned mission is ever sent to Mars, how will the astronauts get oxygen to breathe when they are out there? That is what the next mission, Mars-2020, will try to find out
Has there been life on Mars? – and when a manned mission is ever sent to Mars, how will the astronauts get oxygen to breathe when they are out there? That is what the next mission, Mars-2020, will try to find out
Cosmic grains of dust formed in supernova explosion
9 July 2014
 New research from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen and Aarhus University shows that not only can grains of dust form in gigantic supernova explosions, they can also survive the subsequent shockwaves they are
New research from the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen and Aarhus University shows that not only can grains of dust form in gigantic supernova explosions, they can also survive the subsequent shockwaves they are
New insights into gamma-ray Burst afterglows
30 April 2014
 Gamma-ray bursts are powerful bursts of gamma radiation in connection with the explosive death of massive stars. The bursts themselves are short lived – typically less than a few minutes, but is followed by an afterglow that can be
Gamma-ray bursts are powerful bursts of gamma radiation in connection with the explosive death of massive stars. The bursts themselves are short lived – typically less than a few minutes, but is followed by an afterglow that can be
Cosmic collision creates mini-planet with rings
26 March 2014
 Until now, rings of material in a disc have only been observed around giant planets like Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and especially Saturn, which is known for its spectacular rings. Now astronomers from NBI, have observed the first
Until now, rings of material in a disc have only been observed around giant planets like Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune and especially Saturn, which is known for its spectacular rings. Now astronomers from NBI, have observed the first
Stream of stars in Andromeda satellite galaxy shows cosmic collision
23 February 2014
 The Andromeda Galaxy is surrounded by a swarm of small satellite galaxies. Researchers from NBI, among others, have detected a stream of stars in one of the Galaxy’s outer satellite galaxies, called Andromeda II.
The Andromeda Galaxy is surrounded by a swarm of small satellite galaxies. Researchers from NBI, among others, have detected a stream of stars in one of the Galaxy’s outer satellite galaxies, called Andromeda II.
First images of star cluster from the Gaia Satellite
7 February 2014
 The Gaia Satellite has already sent its first images down to Earth approximately 40 days after its launch on the 19th of December. They show a dense collection of stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud at a distance of 170,000 light years.
The Gaia Satellite has already sent its first images down to Earth approximately 40 days after its launch on the 19th of December. They show a dense collection of stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud at a distance of 170,000 light years.
Early galaxies grew massive through collisions
29 January 2014
 New research from the Niels Bohr Institute shows that massive galaxies were formed by explosive star formation that was set in motion by the collision of galaxies a few billion years after the Big Bang
New research from the Niels Bohr Institute shows that massive galaxies were formed by explosive star formation that was set in motion by the collision of galaxies a few billion years after the Big Bang
