CXC: Cross-disciplinary X-ray Center
The CXC hosted jointly by the Niels Bohr Institute and the Department of Food Science operates two SAXS/WAXS instruments used for structural investigations at the nanometer scale of samples from all areas of material science and caters for users from academia and industry alike.
Interested parties are encouraged to request time for experiments using the form at the bottom of this page although first time users are encouraged to contact the facility manager first for a feasibility assessment - see below.
The SAXS instruments Ganesha and Nano-inXider are used for structural studies of materials of various kinds, for example polymer systems, nano-particles, food and soft matter systems, bio-membranes, liquid crystals, biomacromolecules in solution and many more. There are in principle no limits to the form of the samples - we can handle liquids, gels, pastes, powders, films and solids alike.
However, for users particularly interested in weakly scattering biomacromolecules in solution, we recommend contacting our sister facility, CPHSAXS, at the Department of Drug Design and Pharmacology.
Description
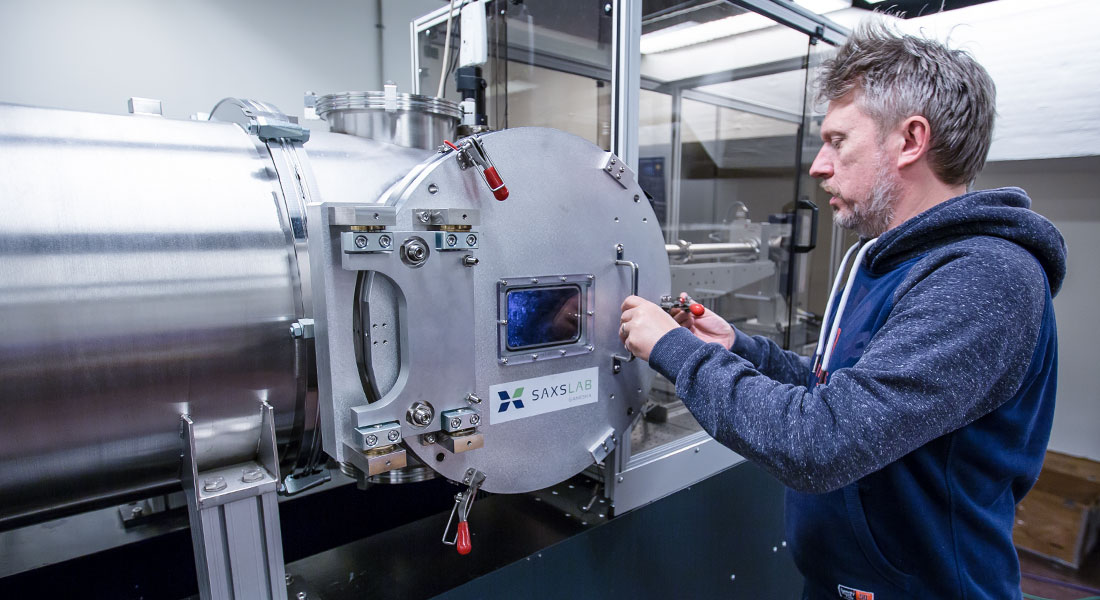
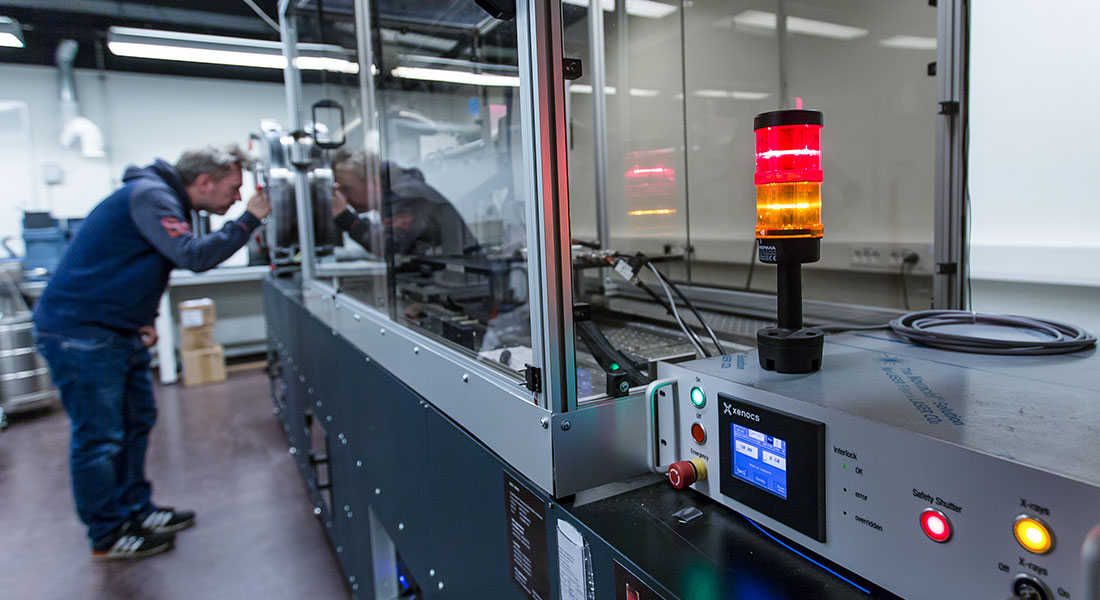
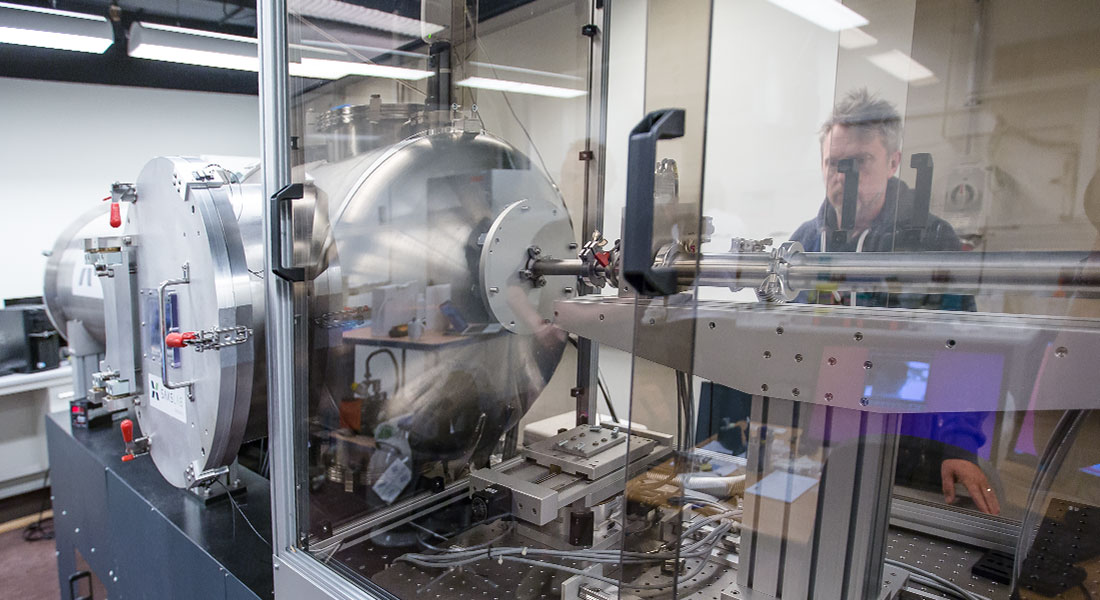
The SAXS instrument at the Niels Bohr Institute comprises a next-generation SAXS instrument using advanced networked instrument control and data analysis. The instrument is fully automated and remotely controllable with capability of performing SAXS, MAXS, WAXS, and GISAXS on both isotropic and oriented samples.
Source
The X-ray source is a 40W micro-focus Cu-sources, Micromax 002+, from Rigaku . The X-ray wavelength is 1.54 Å. The collimator is based on the two motorized scatter-less slits configuration.
Sample environment
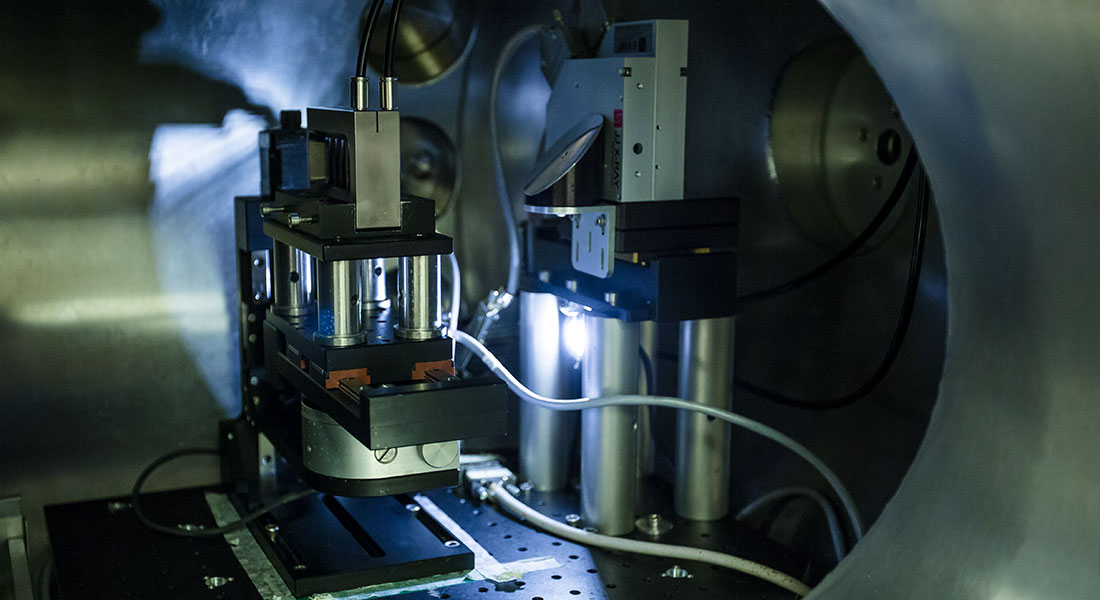
The SAXS instrument has two sample stage positions: I) a large spacious sample area inside the detector-tube allowing for a variety of sample environments and specialized measurement techniques; and II) a sample area before the main vacuum tank allowing measurements both in vacuum and air.
This area can be fitted with for example an Anton Paar type of sample environment dedicated for solution samples with a) easy access to the sample without breaking the vacuum and allowing flow-through type of sample cells or b) small-volume samples (20 mul).
Other options are RheoSAXS or extensional rheology setups. Both sample areas allows for complex, specialed setups to be installed.
Detector
The Pilatus 300k pixel-detector is situated inside a large continuous vacuum chamber, where its position can be controlled to adjust the distance between sample and detector. This allows access to structural studies from few Angstrom-level to several hundred nanometers spanning both the best SAXS instruments and standard WAXS range.
Software
The overall instrument and data acquisition is based in Spec, which is a UNIX/Linux based software package. The initial 2D data from the detector is read-out using Dectris-software.
The motors are controlled using an 18-axis JJ-Motor Controller. SAXSGUI, based on a MATLAB platform, is used for further data reduction and analysis routines.
Acknowledgements
The SAXSLab camera at NBI is a GANESHA-camera designed by Karsten Joensen, SAXSLab/JJ-Xray, and funded by FNU, The Danish Science Council for Nature and Universe, The Carlsberg Foundation and The Lundbeck Foundation.
Description
The Nano-inXider instrument located at the Department of Food Science is a vertical-geometry SAXS and WAXS instrument designed for simplicity and high throughput of samples from a wide array of scientific fields. The vertical set up makes the instrument particularly useful for liquids, emulsions, and similar samples from soft matter.
Source
The source of the Nano-inXider instrument is a 30 W microfocus sealed Cu-tube producing X-rays with a wavelength of 1.54 Å. The windowless beam path is under vacuum all the way to the detector for low-noise, high-signal measurements.
Sample environment
The instrument accommodates a number of sample holder and conditions including standard holders for powders and liquids as well as a low-noise flow cell. Sample temperature can be controlled via temperature sample stages allowing users to investigate samples in temperatures ranging from -150 °C to 350 °C.
Detector
Two fixed Dectris Pilatus 3 hybrid photon counting detectors are used continuously and simultaneously, which allows the instrument to acquire SAXS and WAXS up to 2θ = 60°. SAXS measurement are conducted without a beamstop.
Software
The acquisition software with automatic data reduction produces data in absolute units and offers live data visualization during experiments. XSACT (X-ray Scattering Analysis and Calculation Tool) is used for data analysis and subsequent interpretation.
Acknowledgements
The instrument is funded via the FOODHAY initiative and is part of a larger collaboration establishing advanced instrumentation for investigations of samples from soft matter, food science, biology, and health.
Read more about the instrument model here.
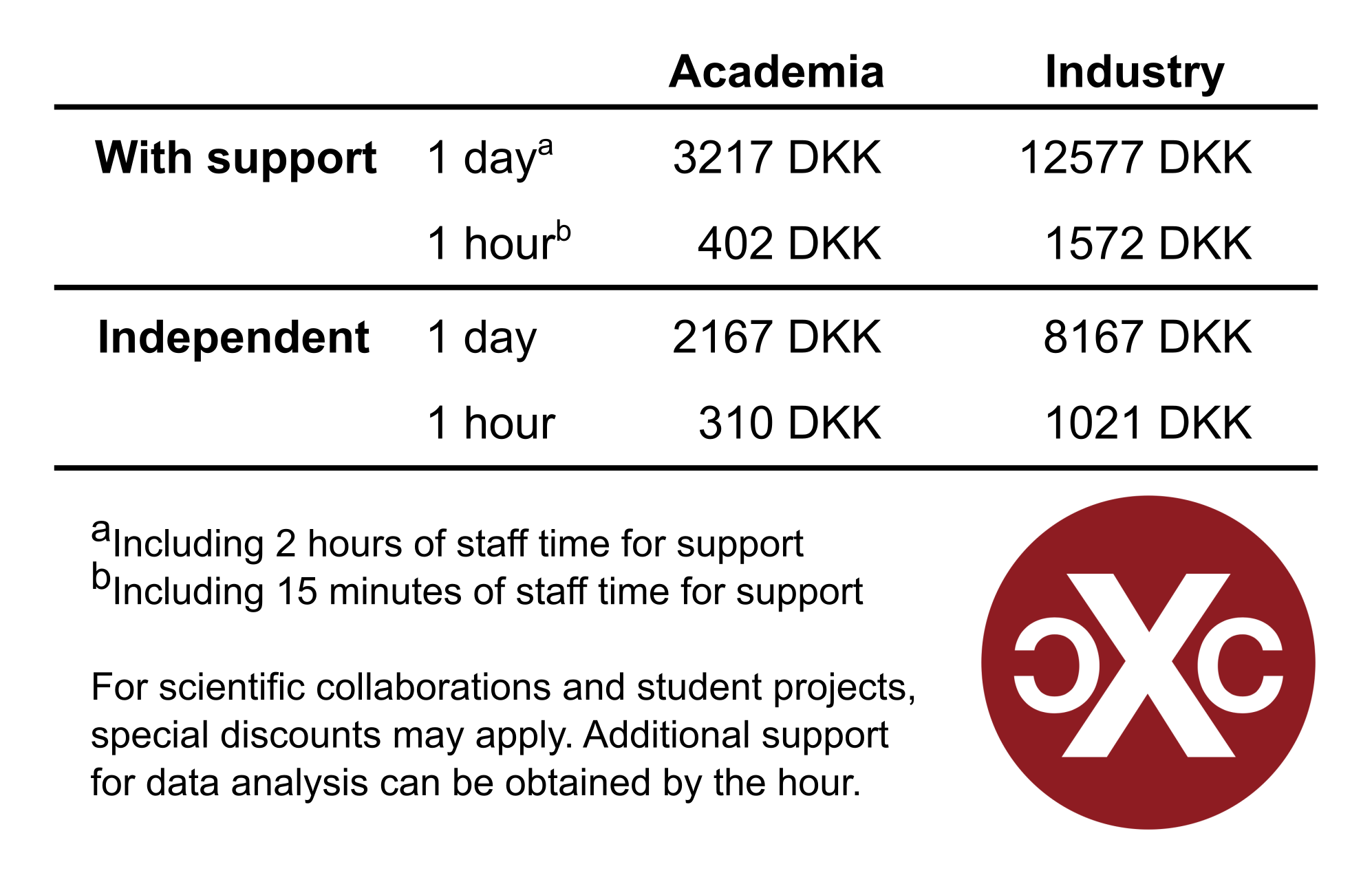
We ask that users contribute to the maintenance and improvement of the instruments. The prices for beam time depend on the amount of support needed and are listed below. Special cases like student projects and feasibility studies should be negotiated directly with the facility manager, see Contact below.
Data reduction and handling
- BioXTAS RAW - GUI based, free, open-source Python program for reduction and analysis of small-angle X-ray solution scattering (SAXS) data
- Primus - Manipulations with experimental 1D small-angle scattering data
- XSACT - X-ray scattering data processing and analysis by XENOCS
Analysis
- SASView - Open source, collaboratively developed software for the analysis of any small angle scattering data
- ATSAS - A program suite for small-angle scattering data analysis from biological macromolecules
- BayesApp - Website with implementation of the BIFT algorithm for computing pair-distance distributions
Nano-inXider
Ganesha
For further information, contact associate professor Jacob Kirkensgaard, jjkk@nbi.ku.dk.