Ramsey Spectroscopy
We want to compare the frequency of our reference oscillator ν osc with the atomic transition frequency ν clock using microwave pulses and measurements.
This can be done with the following 3-step algorithm (Ramsey spectroscopy):
- Prepare the atom in |↓⟩ .
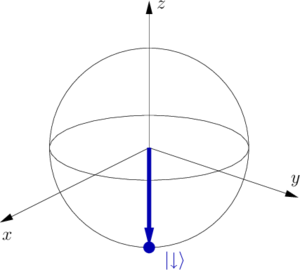
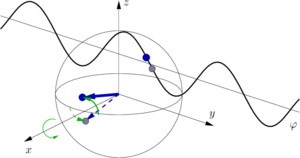
- A microwave π/2 -pulse performs a 90 ∘ -rotation around the y -axis.
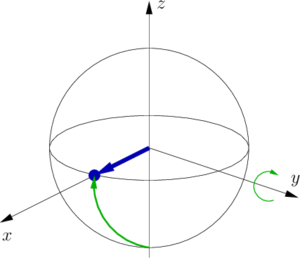
- Now we wait during the interrogation time τ . During this time the state evolves and precesses around the z -axis until φ=τΔν .
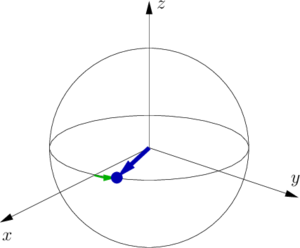
- After the interrogation time a second microwave π/2 -pulse is sent - but this time with a phase such that it performs a 90 ∘ -rotation around the x -axis.
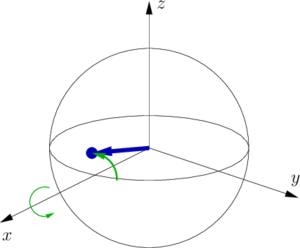
- Finally we measure whether the atom is in the ↓− or ↑ -state. This way - depending on whether Δν was positive or negative - the probability find the atom in either the upper or the lower state is larger and we can adjust the frequency of the reference oscillator ν osc accordingly.
Of course this experiment is not just performed with a single atoms but rather with about 100000 atoms simultaneously.
