Optical Magnetometry for MRI
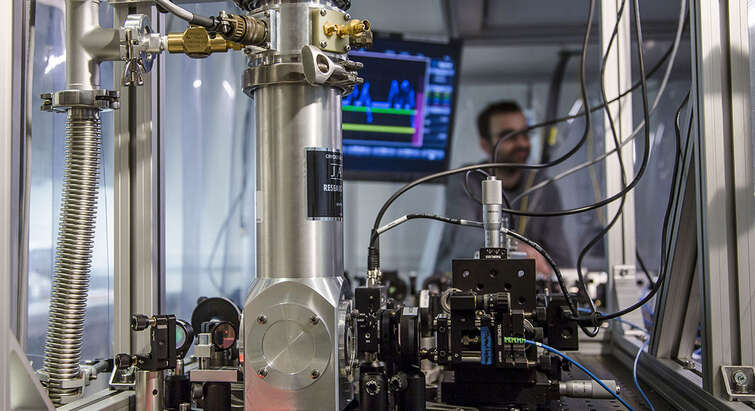
We are developing a fiber-coupled optical magnetometer for use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The optical magnetometer is based on saturated absorption spectroscopy in a cesium vapor.
The work is a collaboration between Quantop (Niels Bohr Institute) and DRCMR (Hvidovre hospital).
- By tracking magnetic field changes during an MRI scan, k-space trajectories can be corrected, leading to improved image quality.
- By using a fiber coupled optical magnetometer, we can measure the field, without introducing electronic equipment, metallic parts, or even wires near the MR scanner. That is, without disturbing the MR scanners operation, or introducing safety hazards.
- The optical magnetometer is being developed in Quantop and is being tested in the 7 T scanner DRCMR.
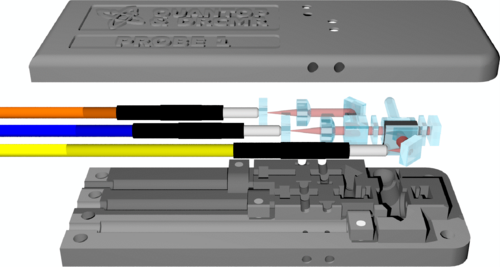
By now 4 probes and a reference have been 3D printed. 3 x 17 m of fibers allow the electronics and the lasers to be placed far from the MRI scanner. The probes are 90 x 33 x 10 mm^3 allowing them to easily be placed in the MR scanner, e.g. inside a head coil for brain scans.
The probes have been calibrated and tested, and the results have been published in the following papers:
- Hans Stærkind et al. High-Field Optical Cesium Magnetometer for Magnetic Resonance Imaging, PRX Quantum 5, 020320, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.5.020320
- Hans Stærkind et al. Precision Measurement of the Excited State Landé g-factor and Diamagnetic Shift of the Cesium D2 Line, Phys. X 13, 021036, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.13.021036
We will proceed to demonstrate that this can be truly useful in medical diagnostics, by improving image quality. This would equip radiographers with a more powerful tool for producing sharp images of the human body, allowing for better diagnostics of a wide range of diseases.
The work received broad attention in international media in early 2024, following the publication in PRX Quantum:
- https://politiken.dk/danmark/sundhed/art9886274/Ny-sensor-skabt-af-dansk-forsker-kan-forbedre-MR-teknologi
- https://www.berlingske.dk/danmark/ny-sensor-skabt-af-dansk-forsker-kan-forbedre-mr-teknologi
- https://healthcare-in-europe.com/en/news/sensor-detect-error-mri-scans.html
- https://www.itnonline.com/content/young-researcher-has-created-sensor-detects-errors-mri-scans
- https://www.science-et-vie.com/technos-et-futur/irm-un-jeune-chercheur-a-cree-un-capteur-pour-detecter-les-fluctuations-magnetiques-et-ameliorer-les-images-135468.html
- https://optics.org/news/15/5/11